Understanding what high blood sugar does to your body
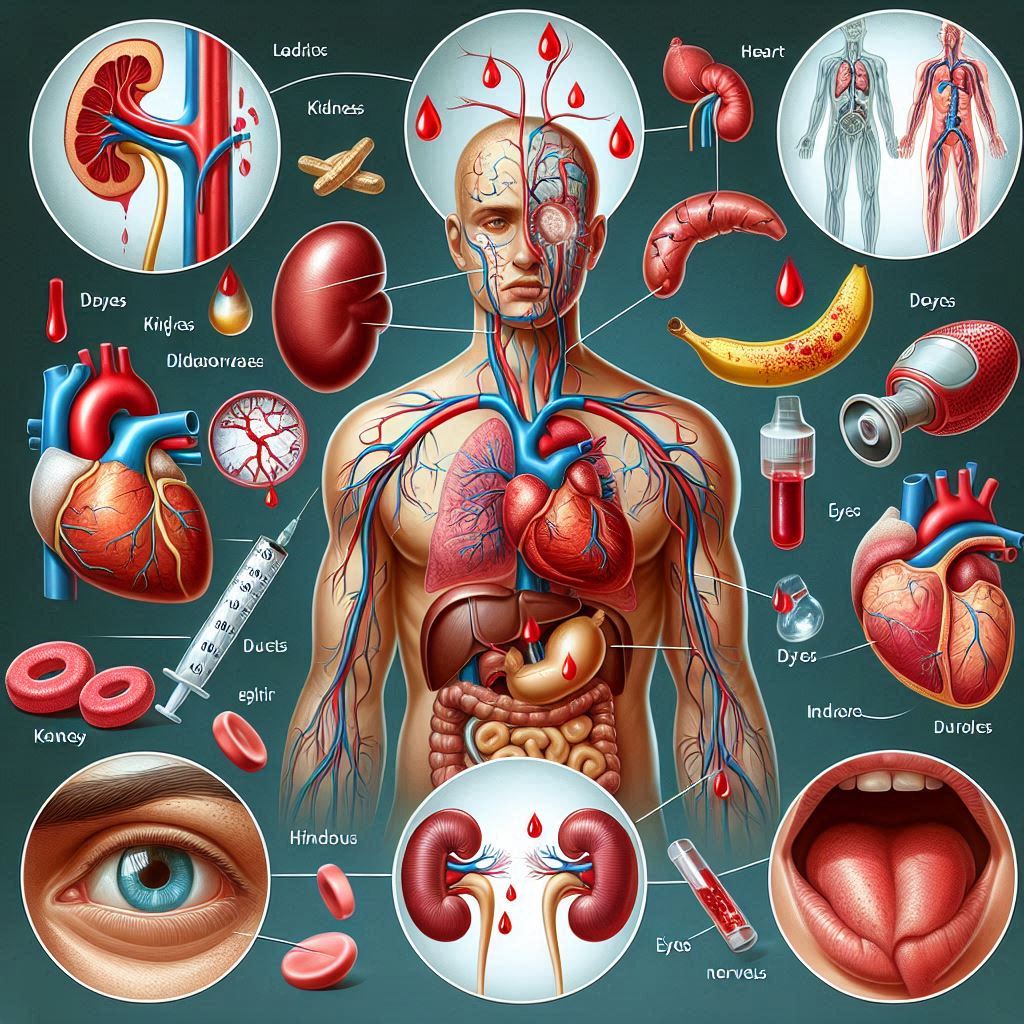
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, is an increasingly common issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding what high blood sugar does to your body is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing serious complications.
High blood sugar levels can lead to a variety of health issues, both in the short and long term. The body's inability to effectively process glucose can result in damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs, culminating in conditions such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and diabetic retinopathy.
- How blood sugar levels affect your body
- What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
- How does high blood sugar affect your overall health?
- What causes high blood sugar levels?
- How to reduce blood sugar levels immediately?
- What level of blood sugar is considered dangerous?
- How do you feel when your blood sugar is too high?
- What to do when blood sugar is high?
- Normal blood sugar levels: What you need to know?
- Questions related to the impact of high blood sugar
How blood sugar levels affect your body
When blood sugar levels rise, the body must work harder to use and store glucose. This can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where cells do not respond well to insulin. Over time, this can strain the pancreas, which produces insulin, leading to its dysfunction.
Excess sugar in the bloodstream can also cause inflammation and oxidative stress, contributing to the damage of blood vessels and nerves. This damage can lead to complications such as poor circulation, especially in the extremities, increasing the risk of infections and slow-healing wounds.
Another serious effect of high blood sugar is its impact on the kidneys. These organs filter waste from the blood, but too much glucose can overburden them, potentially leading to kidney disease or failure.
The impact of high blood sugar on the heart is also significant. It can contribute to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the hardening and narrowing of the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Finally, high blood sugar levels can affect mental health, causing symptoms such as irritability, depression, and anxiety. It can also lead to cognitive issues and increase the risk of dementia.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
- Increased thirst and urination due to the excess glucose being flushed out by the kidneys.
- Excessive hunger because the cells are not receiving the glucose they need for energy.
- Fatigue resulting from the lack of glucose being used effectively as a fuel for the cells.
- Blurred vision caused by the swelling of the lenses in the eyes due to high glucose levels.
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections, a sign of the body's weakened ability to heal and fight off bacteria.
How does high blood sugar affect your overall health?
Chronic high blood sugar, known as hyperglycemia, can lead to long-term complications affecting nearly every organ in the body. It is a major contributor to cardiovascular disease, as it can damage the blood vessels that supply the heart and brain.
Neuropathy, or nerve damage, is another common complication, resulting in numbness, pain, and weakness, particularly in the hands and feet. This can lead to a decreased ability to sense injuries, potentially resulting in serious infections.
Retinopathy, which affects the eyes, can lead to vision loss and is one of the leading causes of blindness among adults. High blood sugar can also affect kidney function, increasing the risk of kidney disease.
Gastrointestinal issues can arise from damage to the nerves that control internal organs, leading to problems such as gastroparesis.
The risk of skin conditions, such as bacterial and fungal infections, is also higher with uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
What causes high blood sugar levels?
Lack of insulin or insulin resistance is the most common cause of high blood sugar levels. This can result from conditions such as type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle factors, including poor diet, lack of physical activity, and being overweight, can also contribute to the development of high blood sugar.
Certain medications and illnesses can lead to hyperglycemia by affecting the body's ability to manage glucose levels.
Stress, both physical and emotional, can trigger the release of hormones like cortisol, which can cause blood sugar levels to spike.
Skipping or not taking enough glucose-lowering medication can also result in elevated blood sugar levels.
How to reduce blood sugar levels immediately?
If you experience high blood sugar levels, it's important to act quickly to bring them down. Drinking water can help flush out some of the excess glucose.
Engaging in physical activity is another immediate way to use up glucose and reduce blood sugar levels.
Adjusting your diet, particularly by reducing carbohydrate intake, can help manage blood sugar spikes.
In cases of persistently high levels, it may be necessary to take insulin or other medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
It is also important to monitor your blood sugar closely and regularly to prevent it from reaching dangerously high levels.
What level of blood sugar is considered dangerous?
A blood sugar level exceeding 180 mg/dL post-meal, or a fasting level above 130 mg/dL, is considered high and can be dangerous if it persists.
A blood sugar level of 250 mg/dL or higher can be particularly hazardous and requires immediate medical attention.
Severely high blood sugar levels, especially over 300 mg/dL, can lead to acute, life-threatening conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
It's critical to know your individual target blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider and to take steps to keep your levels within that range.
How do you feel when your blood sugar is too high?
High blood sugar can make you feel tired and lethargic due to the inability of glucose to enter the cells and provide energy.
You may feel excessively thirsty and need to urinate more often than usual as your body tries to get rid of the excess sugar.
Other symptoms can include headaches, difficulty concentrating, and a general sense of being unwell.
In more severe cases, high blood sugar can cause fruity-smelling breath, a rapid heartbeat, and even loss of consciousness.
What to do when blood sugar is high?
Take immediate action by drinking water and exercising to help lower your blood sugar levels.
Review your diabetes management plan and consider what factors may have contributed to the spike, such as dietary choices or missed medication.
Check for ketones if your blood sugar is very high, as this can be a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, a serious condition.
Contact your healthcare provider if your blood sugar remains high despite taking corrective actions or if you experience any severe symptoms.
Normal blood sugar levels: What you need to know?
Normal fasting blood sugar levels are typically below 100 mg/dL. Levels between 100 to 125 mg/dL indicate prediabetes, and 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests suggest diabetes.
Post-meal blood sugar levels should be below 140 mg/dL to be considered within the normal range.
Maintaining blood sugar levels within these ranges can help prevent the onset of diabetes-related complications.
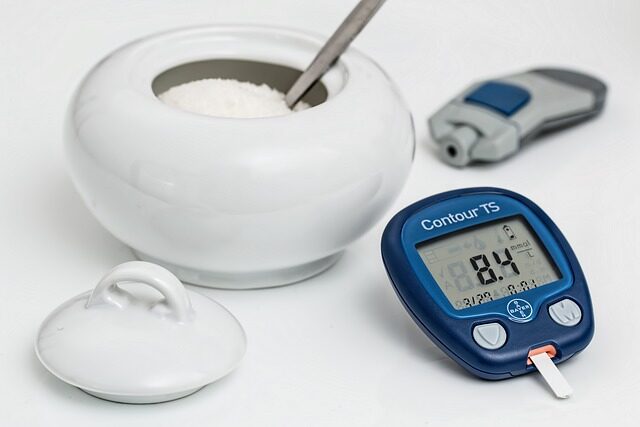
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for those at risk of or living with diabetes.
Discuss with your healthcare provider the best monitoring schedule and target levels for your specific situation.
What happens to the body when blood sugar is too high?
When blood sugar reaches high levels, it can lead to a condition called hyperglycemia. This can cause short-term effects such as dehydration, hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome (HHS), and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) if not managed promptly.
In the long term, sustained high blood sugar can lead to complications like cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney disease, eye problems, and poor wound healing, among others.
How does high sugar affect your body?
High sugar levels in the blood can lead to insulin resistance, where body cells do not respond properly to insulin, making it difficult for the body to regulate blood sugar levels.
It also increases the risk of developing conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and nerve damage, significantly impacting overall health.
How do I bring my blood sugar down immediately?
To lower blood sugar levels quickly, drink plenty of water, engage in moderate physical activity, and consider eating low-glycemic foods that don't spike blood sugar as much.
If you are on insulin or other medications, follow your doctor's advice on how to use them to reduce your blood sugar levels safely.
At what sugar level is diabetic coma?
A diabetic coma, a life-threatening emergency, can occur at blood sugar levels above 600 mg/dL, known as hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS).
However, a diabetic coma can also occur at lower levels if there is a significant imbalance in the body's normal metabolism, such as in DKA or severe hypoglycemia.
Understanding what high blood sugar does to your body and the importance of managing it can help prevent these serious complications. By recognizing the symptoms of high blood sugar and knowing how to respond, you can maintain better control over your health and reduce your risk of long-term damage.

Leave a Reply